About Bone Marrow Transplants
When your blood system is healthy, it’s always making new blood-forming cells. These are necessary for survival. If your body begins making diseased cells or doesn’t make enough healthy cells, a bone marrow or cord blood transplant may be the best treatment and only potential cure.
A marrow transplant is a type of cellular therapy. It also may be called a blood and marrow transplant, a blood or marrow transplant, or a blood stem cell transplant.
Where Do Healthy Cells Come From?
A patient may be able to use their own blood-forming cells. Cells can also be donated from someone else.
An autologous transplant is when a person’s own cells are used. These cells are collected from the patient’s bloodstream and stored for transplant. Autologous transplant may be an option for patients with certain diseases.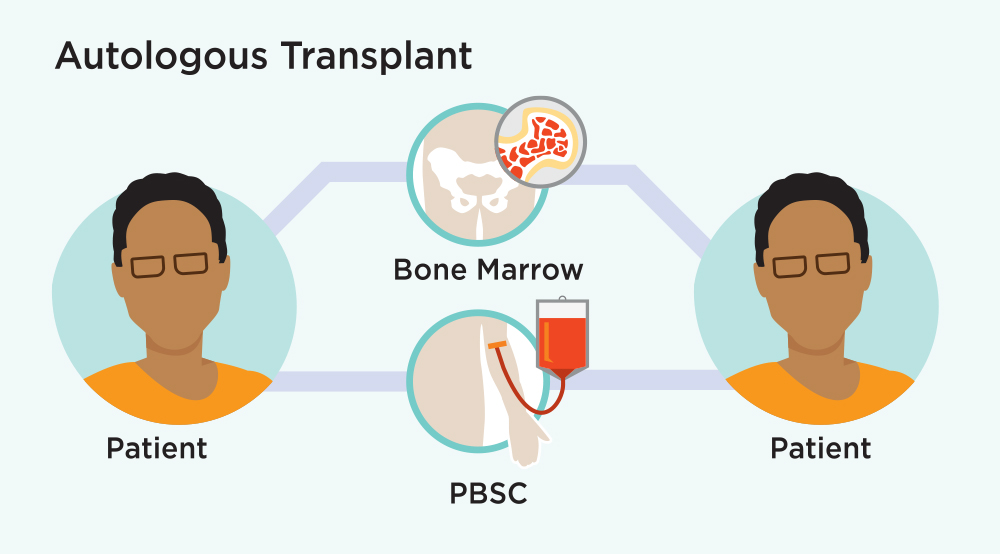
An allogeneic transplant is when cells from a family member, unrelated donor, or umbilical cord blood unit are used for transplant. This is called a related donor transplant if the donor is a family member or an unrelated donor transplant if the donor is not a family member.
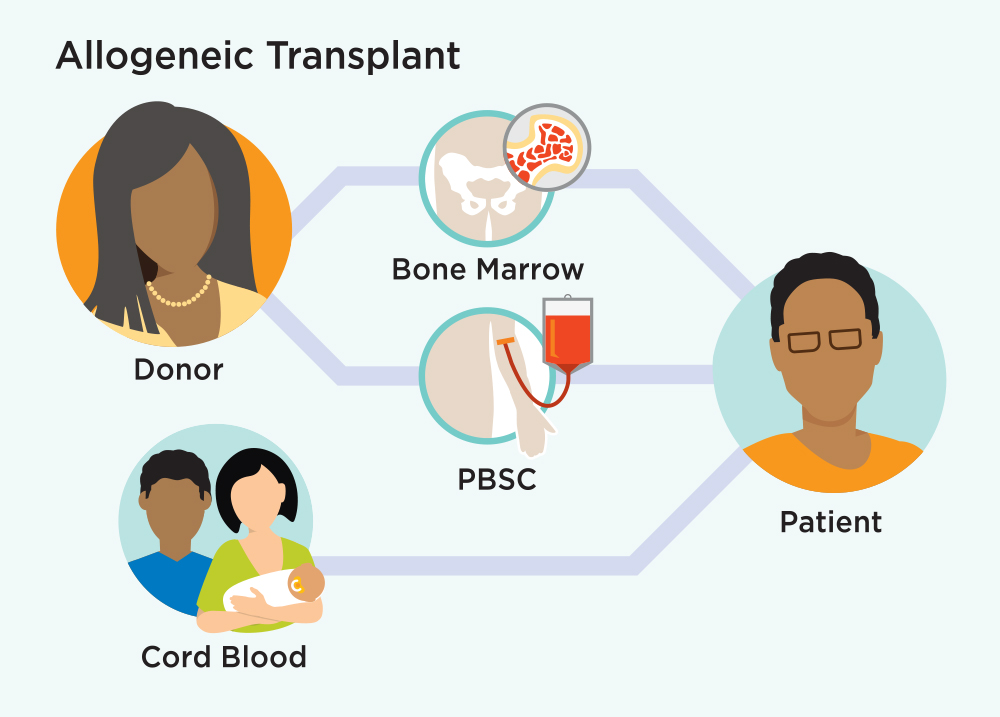
Donated cells can come from three sources:
- Bone marrow
- Peripheral (circulating) blood (also called peripheral blood stem cells or PBSC)
- Blood collected from an umbilical cord after a baby is born
Doctors will choose the best source of cells for a patient. Be The Match® only uses cells voluntarily donated by an adult donor or cells collected from the umbilical cord, which occurs only after a full-term delivery when both mother and baby are healthy and safe.
How a Transplant Works
A bone marrow transplant takes a donor’s healthy blood-forming cells and puts them into the patient’s bloodstream where they begin to grow and make healthy red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. Patients receive high doses of chemotherapy to prepare their body for the transplant. Then on transplant day, the patient receives the donated cells in a process that’s like getting blood or medicine through an intravenous (IV) catheter, or tube.
Diseases Treatable by Transplant
A bone marrow or cord blood transplant may be the best treatment option or the only potential for a cure for patients with diseases such as:
- Leukemias and lymphomas
- Bone marrow diseases and other diseases where bone marrow fails to work, such as severe aplastic anemia
- Inherited immune system disorders
- Hemoglobinopathies (diseases with poorly functioning red blood cells), including sickle cell disease
- Inherited metabolic disorders
- Myelodysplastic syndromes and myeloproliferative disorders
- Multiple myeloma and other plasma cell disorders
- Familial erythrophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis and other histiocytic disorders
- Certain other malignancies or cancers
You can give hope to patients with these diseases and others by joining the marrow donor registry.
